What is High Dynamic Range? Why is It Important for Automotive Cameras?
In our previous blog post “How to Choose the Best Automotive Camera for Outdoor AMR and Unmanned Vehicles,” we shared the key factors to consider when selecting a camera for an outdoor autonomous vehicle. High Dynamic Range is one of these seven critical factors. In this blog post, we’ll take a deeper look at why HDR is so important for automotive cameras, how it works, and how oToBrite addresses the challenges related to cameras for outdoor vehicle applications.
What Is High Dynamic Range (HDR)?
Imagine you’re driving out of a dark tunnel into bright sunlight. The camera needs to see both the bright road ahead and the shaded interior of the tunnel at the same time. A regular camera often struggles in this situation; the bright areas can become completely white, while the dark areas inside the tunnel can turn completely black. This is where high dynamic range comes in.
High dynamic range (HDR) is a technology that allows automotive cameras to capture details in both bright and dark areas at the same time, so nothing important is lost.
How Does High Dynamic Range Work?
In simple terms, high dynamic range allows cameras to capture scenes more like the human eye. For example, when a vehicle is driving at night and bright headlights or streetlights suddenly appear in view, a standard camera without HDR may overexpose those highlight spots and lose important details in darker areas. This can make it difficult for the system to clearly perceive the environment and accurately assess the situation for decision-making.
To address this, HDR technology captures the same scene multiple times in rapid succession at different exposure levels, some brighter, some darker. Then, smart image-processing algorithms combine these shots into one final image, taking the best details from each and balancing details across both highlight and shadow areas.
As a result, automotive cameras can maintain a well-balanced and accurate view of the environment even when lighting changes abruptly, such as when encountering oncoming headlights, reflective traffic signs, or streetlights at night.
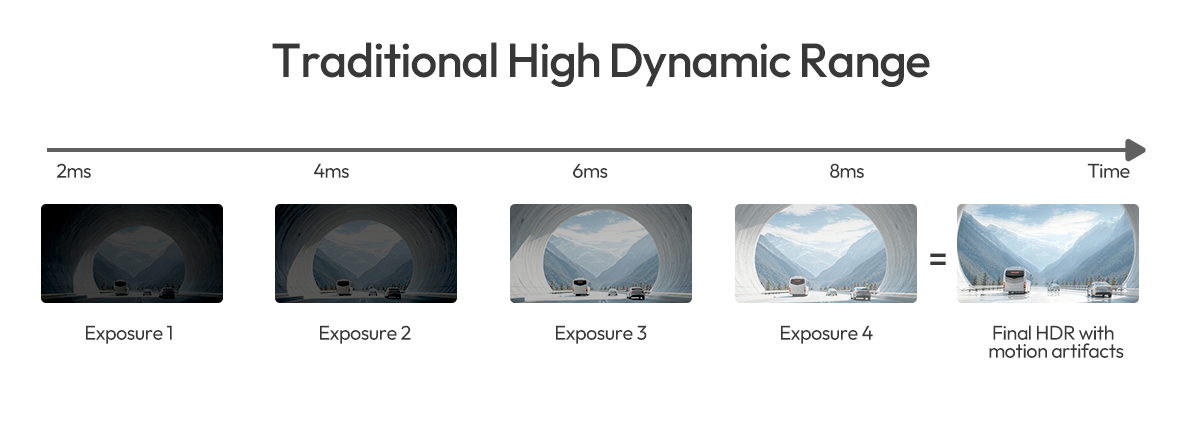
From the Traditional Way to Simultaneous Exposures
While the basic High Dynamic Range process improves image detail by combining multiple exposures, it still faces challenges when objects are moving.
Traditional HDR imaging captures multiple images at different exposure times and combines them into one. While this works well for static scenes, it’s not ideal for automotive applications, where vehicles and objects are constantly moving. Because each exposure is taken sequentially, fast motion between frames can cause motion artifacts, objects may appear blurred, ghosted, or distorted.
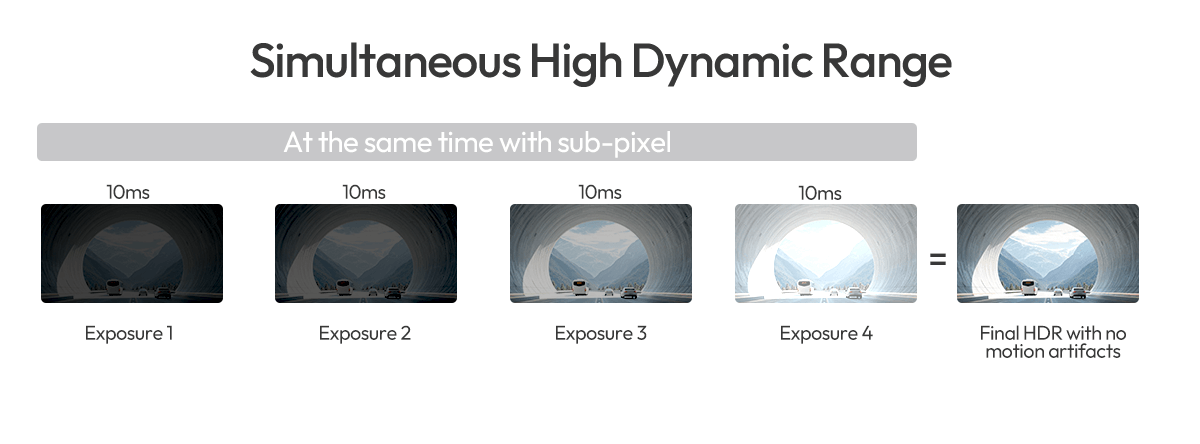
Modern HDR sensors eliminate this issue by capturing multiple exposures simultaneously. With sub-pixel (split-pixel) technology, each pixel includes both large and small photodiodes with different light sensitivities. Combined with dual conversion gain readouts (high and low gain), the sensor effectively collects multiple exposure levels at the same time producing a single, linear HDR output without latency or motion distortion. This simultaneous exposure approach delivers true real-time HDR, ensuring clear and accurate imaging even in fast-changing lighting conditions, exactly what automotive cameras need.
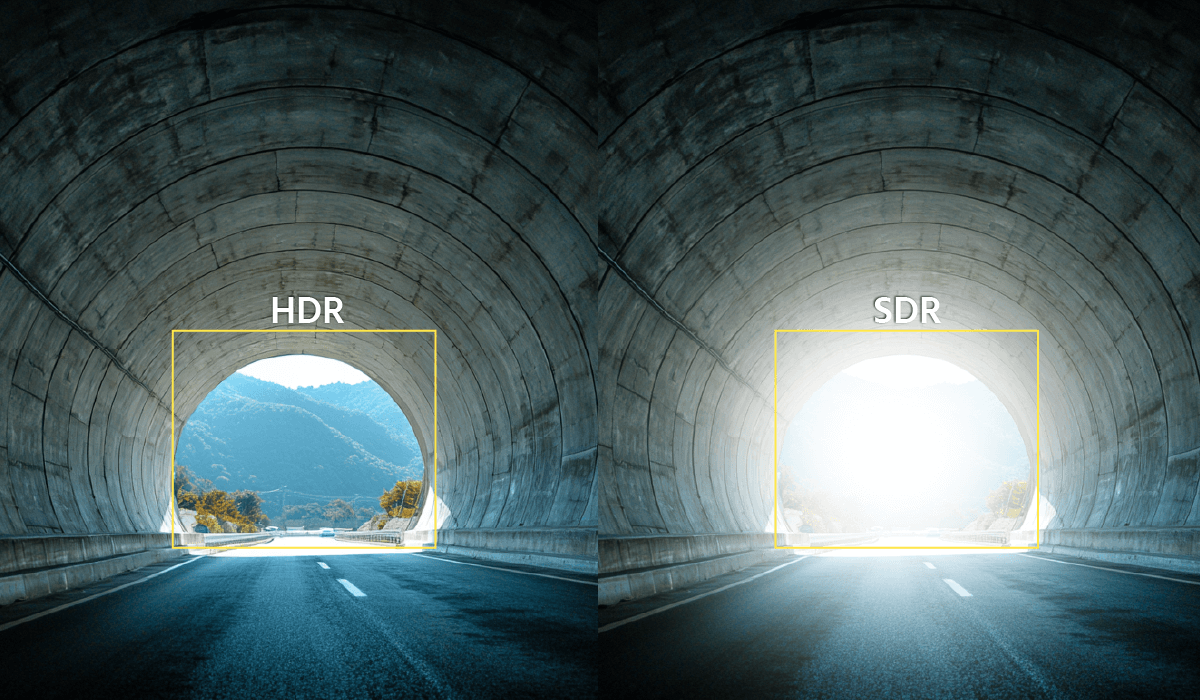
What Is The Difference Between SDR and HDR?
Basically, Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) captures a limited range of light, which can cause bright areas to overexpose and dark areas to lose detail, making it less effective in challenging lighting conditions. On the other hand, High Dynamic Range (HDR) captures a much wider range of light, often using multiple exposures or advanced pixel designs, preserving details in both light and dark regions.
How is High Dynamic Range Measured?
In automotive camera sensors, dynamic range is typically measured in decibels (dB), which represents the ratio between the brightest and darkest light the sensor can capture. A higher dB value means the sensor can handle more extreme lighting differences without losing detail. The dynamic range in dB can be calculated using the formula:
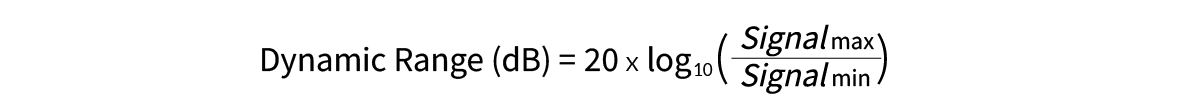
Here, Signalmax is the strongest light the sensor can detect without overexposure, and Signalmin is the weakest signal detectable above noise.
Interestingly, have you ever wondered why people often say that the camera is the “eye of the vehicle”? The reason is that the human eye can perceive a dynamic range of roughly 100 dB, allowing us to see both bright sunlight and deep shadows simultaneously. In automotive applications, camera sensors also must achieve a comparable range of at least 120 dB. Their high dynamic range performance can surpass that of the human eye in extreme conditions, ensuring that the vehicle can “see” clearly and safely at all times.
Why Is High Dynamic Range Important for Automotive Cameras?
1. Challenges in Automotive Camera Applications
High Dynamic Range (HDR) is a very important feature for automotive cameras because these cameras are designed for outdoor vehicle applications, where they face challenges such as rapidly changing lighting conditions from day to night, bright sunlight to dense fog, and from shaded streets to reflective wet roads. Other factors on the road, such as bright headlights and streetlights, can also affect the camera’s ability to capture clear images.
To handle these situations safely, automotive cameras must be able to capture both bright and dark details simultaneously, providing clear visual information for the vehicle’s perception system. This ensures that, whether the vehicle is ADAS-equipped or fully autonomous, the system receives accurate and reliable data for processing and decision-making.
Read more: What is ADAS? Features, Sensors, and Levels of Driving Automation Explained
2. Key Benefits of High Dynamic Range in Automotive Cameras
- Accurate Object Detection: Detect pedestrians, vehicles, traffic signs, and obstacles clearly, even under extreme or rapidly changing lighting.
- Improved Lane and Road Visibility: Maintain clear lane markings and road details in shadows and bright sunlight.
- Enhanced Safety in Challenging Lighting: Handle sudden transitions from dark tunnels to bright roads without losing important visual information.
- Reliable Input for ADAS and Autonomous Systems: Provide perception algorithms with consistent, high-quality images to reduce errors and improve decision-making.
How oToBrite Ensures Reliable Image Performance

At oToBrite, every automotive camera is designed to deliver the highest image quality for real-world driving environments. Our cameras primarily use Sony and onsemi sensors, both known for excellent low-light performance and wide dynamic range. All camera models support a high dynamic range of 120 dB, while those using the AR0823 sensor can achieve up to 150 dB, ensuring clear image capture even under extreme lighting conditions.
Beyond sensor performance, oToBrite further enhances image quality through several in-house capabilities:
- Image Quality Tuning: Fine-tuning of ISP (Image Signal Processor) parameters to optimize color balance, contrast, noise reduction, and HDR tone mapping for automotive perception systems.
- Active Alignment Equipment: Precision assembly to ensure the lens and sensor are perfectly aligned, minimizing optical distortion and improving sharpness.
- Intrinsic Calibration Service: Calibrating camera parameters to ensure accurate geometric and color consistency is critical for applications like sensor fusion and 3D perception.
Together, these capabilities enable oToBrite cameras to deliver reliable, high-quality images that meet the demanding requirements of outdoor vehicle applications such as self-driving cars, autonomous trucks, delivery robots, shuttle buses, etc.
Ready to experience true high dynamic range performance? Explore the full suite of oToBrite camera systems now → oToBrite Camera Selector, or if you need consultation for any in-house service, do not hesitate to contact us.
FAQs
1. What is dynamic range?
Dynamic range refers to the ratio between the brightest and darkest parts of an image that a camera sensor can capture at the same time.
2. What is high dynamic range?
High Dynamic Range (HDR) is a technology that increases the camera’s dynamic range, allowing it to record details in both very dark and very bright areas simultaneously.
3. Is high dynamic range good for your eyes?
High dynamic range itself does not directly affect human eyesight. It is a technology for capturing or displaying images with a wider range of brightness, making visuals look more natural and detailed
4. Is high dynamic range (HDR) the same across cameras, TVs, and smartphones?
People often wonder if HDR works the same way in all devices. But the answer is NO; the principle is similar (capturing or displaying a wider brightness range), but implementation varies depending on sensors, displays, and processing pipelines.
5. Does HDR alone ensure good image quality?
No. While HDR greatly improves visibility in scenes with extreme lighting by preserving details in bright and dark areas, it is only one factor in overall image quality. Other aspects, such as sensor resolution, low-light performance, lens quality, and image signal processor, also play a crucial role in producing clear, sharp, and accurate images.



